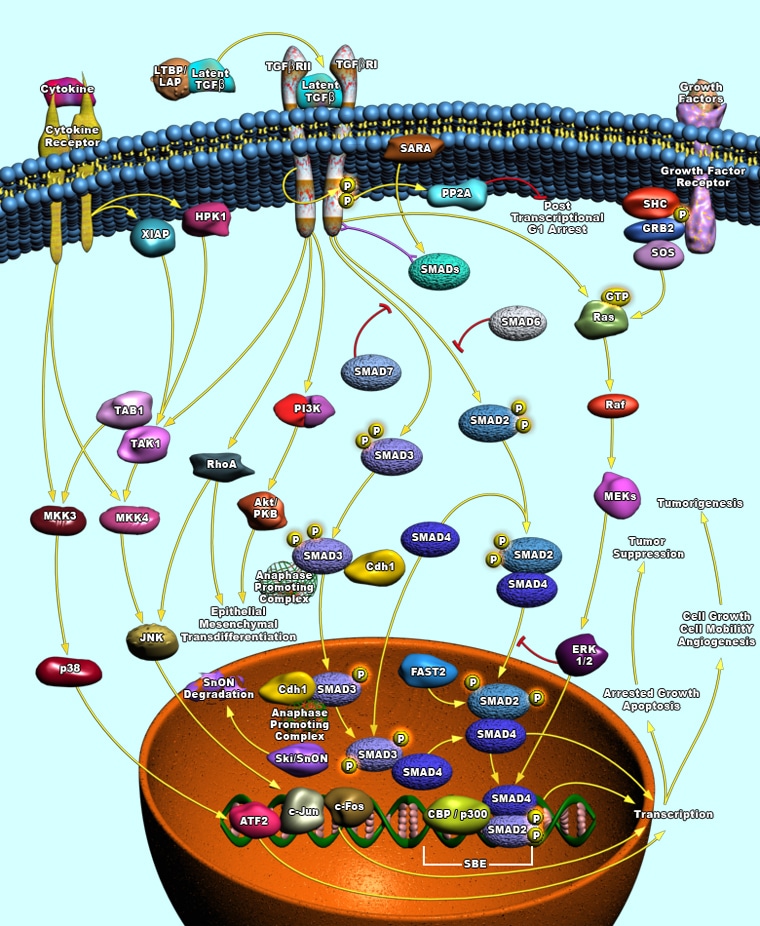
TGF-beta Signaling Pathway
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling plays a key role tissue homeostasis, which is accomplished through dynamic regulation of many cellular processes, including cell growth, migration, differentiation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and extracellular matrix remodeling. Generally, signaling is initiated with the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic Smad signaling molecules, which results in their translocation to the nucleus where they modulate transcription. TGF-βs are often overexpressed in many disease states such as fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer.

Related Products
Featured Publications
Xue G., Restuccia DF., Lan Q., et al. Akt/PKB-mediated phosphorylation of Twist1 promotes tumor metastasis via mediating cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and TGF-? signaling axes. Cancer Discov. 2012 Mar;2(3):248-59. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0270.
Species: Human
Sample type: Conditioned Media (4T1 conditioned cells)
View Publication
Lippert E., Falk W., Bataille F., et al. Soluble galectin-3 is a strong, colonic epithelial-cell-derived, lamina propria fibroblast-stimulating factor. Gut . 2007 Jan;56(1):43-51. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.081646. Epub 2006 May 18.
Species: Human
Sample type: Conditioned Media (Colonic Epithelial Cells')
View Publication