Obesity Proteomics
Tools to study the molecular dynamics of obesity
Obesity and the diseases arising from it (diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer) constitute a major health challenge to the industrialized world. In the past decade, it has become apparent that adipose tissue is not an inert fat-storage depot, but a major endocrine organ which secretes numerous soluble factors and regulates many processes related to glucose homeostasis, lipid and protein metabolism, hunger/satiety, inflammatory and immune responses, and vascular function. Collectively, these factors are referred to as adipokines. Some are mainly produced by adipose tissue (e.g., leptin and resistin), while others are classical cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, and IL-1, which are also synthesized in other tissues. Understanding adipokine-mediated molecular signaling is critical to understanding and treating the myriad of diseases resulting from obesity.
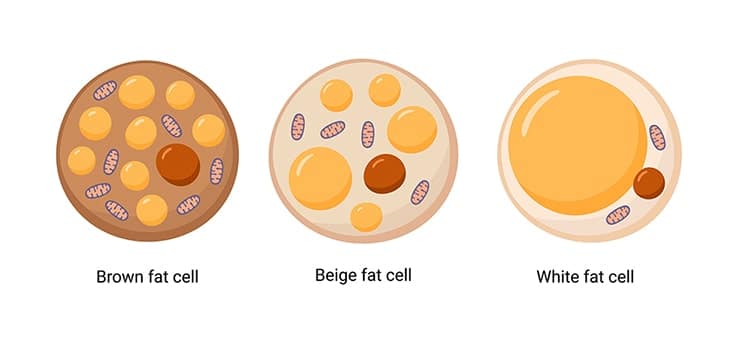

Adipocytes are divided into three cell types, white, brown, and beige. White adipocytes are the most abundant, brown are highly metabolically active, and beige can initiate non-shivering thermogenesis.
Antibody based detection tools
RayBiotech offers multiple formats to fit obesity proteomics to your experimental design. Platforms are pre-developed and can be customized to your targets of interest. We offer multiple multiplex and singleplex proteomic options.
Related Products
Featured Publications
When publishing with RayBiotech, you are eligible for the “Publication30 ” 30% off discount. Following purchase, you can post a review for an amazon gift card.
Jung YJ, Kim HK, Cho Y, Choi JS, Woo CH, Lee KS, Sul JH, Lee CM, Han J, Park JH, Jo DG, Cho YW. Cell reprogramming using extracellular vesicles from differentiating stem cells into white/beige adipocytes. Sci Adv. 2020 Mar 25;6(13):eaay6721. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay6721. PMID: 32232152; PMCID: PMC7096171.
View Publication
Dai Y, Wu X, Dai D, Li J, Mehta JL. MicroRNA-98 regulates foam cell formation and lipid accumulation through repression of LOX-1. Redox Biol. 2018 Jun;16:255-262. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 8. PMID: 29549823; PMCID: PMC5952997.
View Publication
Maixner, N., Pecht, T., Haim, Y., et al. A TRAIL-TL1A Paracrine Network Involving Adipocytes, Macrophages, and Lymphocytes Induces Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Downstream of E2F1 in Human Obesity. Diabetes. 2020 Nov;69(11):2310-2323. doi: 10.2337/db19-1231.
View Publication
Unamuno X, Gómez-Ambrosi J, RamÃrez B, RodrÃguez A, Becerril S, Valentà V, Moncada R, Silva C, Salvador J, Frühbeck G, Catalán V. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces adipose tissue inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019 Sep 24. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0296-z. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 31551515.
View Publication
Related Research Areas
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a medical term that comprehensively describes a range of disorders of the heart and/or blood vessels. These disorders differ markedly in physical implications, time-scale of development, and relative contributory effects of genes and environment.